Lesson G5: Collections#
In this lesson we will learn about the Java Collection Framework. There are many abstract classes, concrete classes, and interfaces that make up the framework.
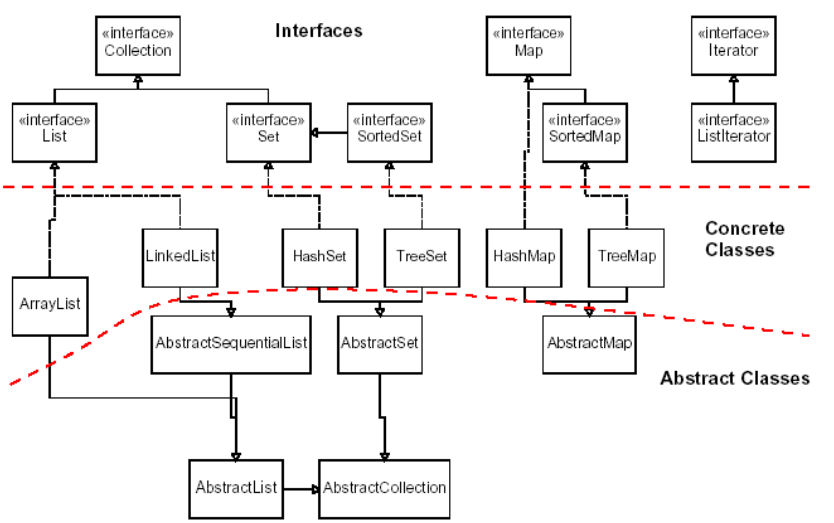
We will look at a class hierarchy showing interfaces, abstract classes, and concrete classes. The point is to see how code is shared by using the abstract classes, and behaviors are provided by classes not necessarily in the same path.
We also want to review the most fundamental data structures.
Lists, Sets and Maps#
The most popular Collection classes are Lists, Sets and Maps.
As we’ve seen, a List behaves like a dynamically sized array. One can index into it using integer values (e.g. list.get(3)). The list has order as the items are stored at indices 0 to n.
Index |
Element |
|---|---|
0 |
Item0 |
1 |
Item1 |
2 |
Item2 |
3 |
Item3 |
A Set is a very simple collection of object. It is very much like a set in mathematics. There is no order to the items. The main thing you do with a set is to add and remove items. You can also clear it, get its size, and see if the set contains an item already.
This is a Set |
|---|
{ Item2, Item1, Item0, Item3 } |
A Map behaves like an array where the index must be an Object instead of an int. See Maps

Quick Summary#
There are many Collection classes. Here are the top three types.
Collection |
Description |
Example Concrete Class |
|---|---|---|
List |
Like an array, but it grows and shrinks, and has helper methods. |
ArrayList<String> |
Set |
Like a List, but no duplicates are allowed. |
HashSet<String> |
Map |
Like a List, but the index can be any Object |
HashMap<String> |
Fundamental Structures#
We will use conceptual names that map to interfaces. And we will show the most popular types of classes used to implement that behavior.
Type |
Class |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
List |
ArrayList |
|
LinkedList |
||
Queue |
LinkedList |
|
ArrayDeque |
||
Stack |
Stack |
|
LinkedList |
Acts as both a Stack and a Queue via interface |
|
ArrayDeque |
Acts as both a Stack and a Queue via interface |
|
Set |
HashSet |
|
TreeSet |
||
Map |
HashMap |
|
TreeMap |
Here we see the class hierarchy of many classes in the Java Collections Framework.